What is DMA – Direct Memory Access – How Does DMA Work?
What is DMA? Direct Memory Access. DMA Controller. How Does Direct Memory Access DMA Work?
Direct Memory Access Controller is referred to as DMA.
DMA is a system peripheral and bus master that enables fast data transfers between memory and peripherals as well as from memory to memory.
DMA moves data fast and without using CPU power, freeing up CPU resources for other tasks.
In the contemporary digital world, data is constantly transmitted between computers and devices. Nevertheless, the rate at which computer systems can process data is finite. Therefore, with the growth of numerous devices, including printers, high-speed modems, and sensors, data processing has turned into a bottleneck.
The CPU won’t be able to do any other tasks at the same time if it is handling all data transfers. Direct memory access (DMA) controllers were created as a solution to this issue. It allows two devices to transfer data without using the CPU.
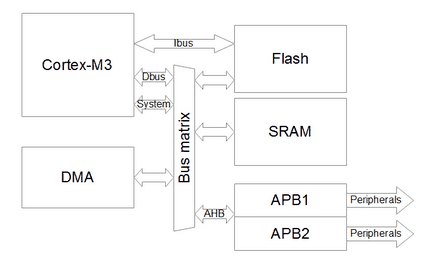
How Does DMA Work?
Data is sent via DMA channels from the system memory to a peripheral device that is connected. A bus line, which is also used for DMA channels, connects system resources such the CPU, memory, associated I/O devices, and a DMA controller. Memory addresses are generated and read/write cycles are initiated by the DMA controller.
The CPU instructs the DMA controller to associate a memory address for use and start a data transfer. The read/write lines and destination addresses to the system memory are set by the DMA controller. After that, until a whole block of data is transferred, it modifies the internal memory address for each byte of data that is transferred.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DMA
| Advantages of DMA | Disadvantages of DMA |
| Speed up data transfer and memory operations. | Requires to carry out the additional operations, which increases the cost |
| Don’t involve CPU during data transfer | The added complexity of the software |
| The workload is appropriately distributed | Additional cost of the hardware |
| Helps in decreasing the load on the CPU | Suffers from cache coherence problem |
| Needs only a few number of clock cycles while transferring data | The device initiating the transfer must be able to communicate with other devices |
| Efficient in facilitating direct data transfer between two devices operating at different speeds | Both devices must be able to initiate the data transfer independently |
| Allow efficient use of interrupts | A computer system connected to a network computer (NC) can’t use a DMA controller |
Please refer to our Nucleo DMA example for a demonstration.



