6-Examples for Loops and Program Control in C
C Programming Lessons, Learn C Programming, Introduction to C Language, How to Program with C
This course will examine more detailed example programs on structured programming, loops, and program control, covered in previous lectures.
For Loop Examples
/***** Program to find the sum of all even numbers from 2 to 100 ****/
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int sum=0, number; //defining variables
for(number=2; number<=100; number+=2) //starting from 2 to 100 incresing 2 by 2
{
sum+=number; //can be written also sum=sum+number ,
//each loop cycle adds every even number to sum variable
}
printf("Sum = %d\n",sum); //prints sum of the even numbers between 2-100
return 0;
}
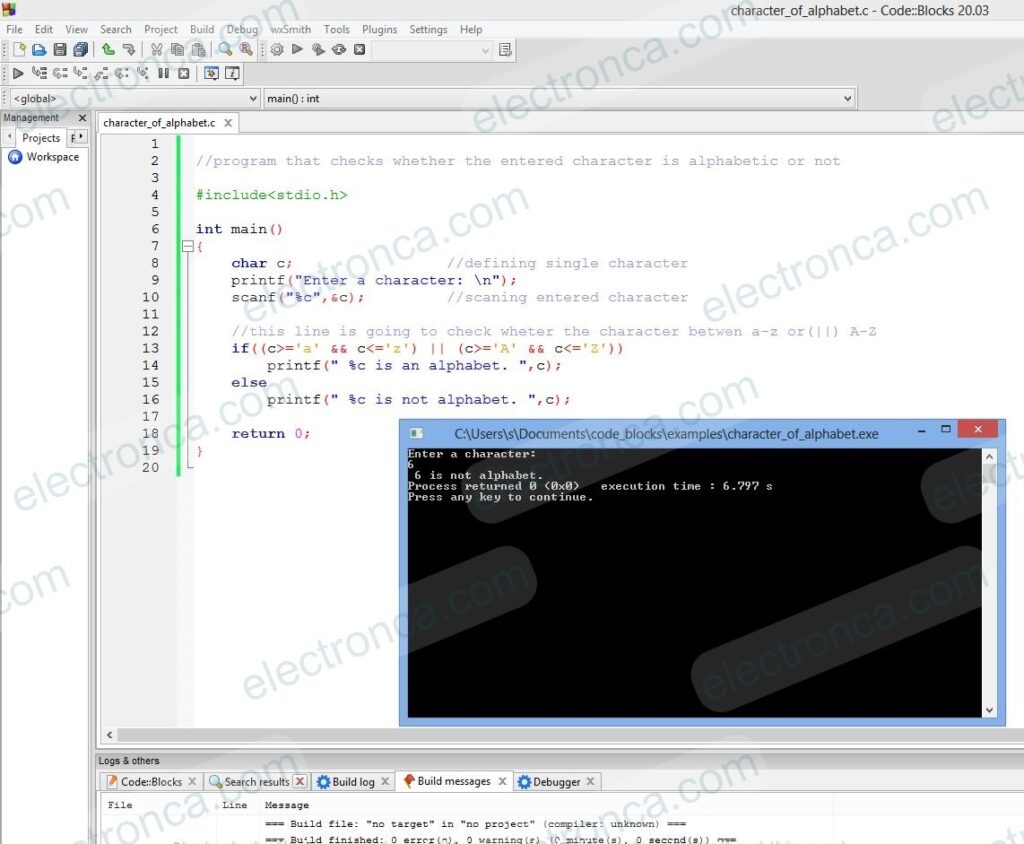
//program that checks whether the entered character is alphabetic or not
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char c; //defining single character
printf("Enter a character: \n");
scanf("%c",&c); //scaning entered character
//this line is going to check wheter the character betwen a-z or(||) A-Z
if((c>='a' && c<='z') || (c>='A' && c<='Z'))
printf(" %c is an alphabet. ",c);
else
printf(" %c is not alphabet. ",c);
return 0;
}

/***program to print numbers, increasing number per line*////
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i=0; i<=10; i++) // i increase to reach 10
{
for(int j=0; j<=i; j++) //nested for loop,
//j increase to reach i at every loop cycle
{
printf("%d ",j);
}
printf("\n"); // to pass one line below at each cycle of i
}
return 0;
}

While Loop Examples
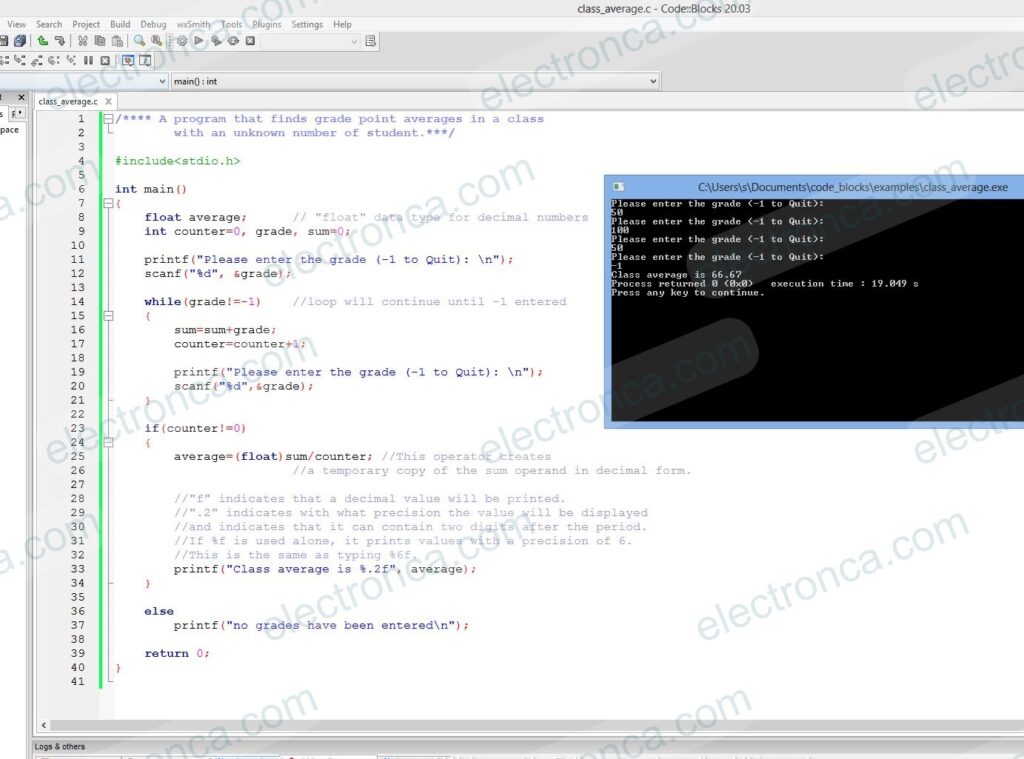
/**** A program that finds grade point averages in a class
with an unknown number of student.***/
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
float average; // "float" data type for decimal numbers
int counter=0, grade, sum=0;
printf("Please enter the grade (-1 to Quit): \n");
scanf("%d", &grade);
while(grade!=-1) //loop will continue until -1 entered
{
sum=sum+grade;
counter=counter+1;
printf("Please enter the grade (-1 to Quit): \n");
scanf("%d",&grade);
}
if(counter!=0)
{
average=(float)sum/counter; //This operator creates
//a temporary copy of the sum operand in decimal form.
//"f" indicates that a decimal value will be printed.
//".2" indicates with what precision the value will be displayed
//and indicates that it can contain two digits after the period.
//If %f is used alone, it prints values with a precision of 6.
//This is the same as typing %6f.
printf("Class average is %.2f", average);
}
else
printf("no grades have been entered\n");
return 0;
}
/*********************************************
A course prepares students for an exam.
There is a list of 10 students.
It says 1 if he passed the exam, 2 if he failed.
Requested from us;
1) "Enter Result" message will be written
2) exam result numbers will be found
3) how many people passed and how many failed
4) If more than 8 passes, it will say "high success"
*****************************************************/
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int passed=0, failed=0, student=1, result;
while(student<=10)
{
printf("Enter the result (1=pass,2=fail): ");
scanf("%d", &result);
if(result==1)
passed=passed+1; //counts passed number of students
else
if(result==2)
failed=failed+1; //counts failed number of students
student=student+1; //student counter
}
printf("%d passed\n",passed);
printf("%d failed\n", failed);
if(passed>8)
printf("High success\n");
return 0;
}

Switch Multi-Select Structure
Let’s explain the switch-case structure we mentioned in our 4th article with an example here.
An algorithm may include a number of choices, such as comparing a variable or expression with individual constants and performing different operations accordingly. C can make such selection structures with the switch multi-selection structure.
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
char grade; //defining variable
printf("Enter your grade: \n");
scanf("%c",&grade); //saving entered grade
switch(grade)
{
case 'A': case'a' : //if grade in uppercase or lower case
printf("Excellent!\n" );
break;
case 'B' : case'b':
case 'C' : case'c':
printf("Well done\n" );
break;
case 'D' : case'd':
printf("You passed\n" );
break;
case 'F' : case'f':
printf("Better try again\n" );
break;
default :
printf("Invalid grade\n" );
}
printf("Your grade is %c\n", grade ); // printing grade on screen
return 0;
}

/***simple calculator with basic operations using switch-case***/
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num1,num2;
float result=0;
char opr; //to store operator choice
printf("Enter first number: \n");
scanf("%d",&num1);
printf("Enter second number: \n");
scanf("%d",&num2);
printf("Choose operation to perform (+,-,*,/,%): \n");
scanf(" %c",&opr);
switch(opr)
{
case '+':
result=num1+num2;
break;
case '-':
result=num1-num2;
break;
case '*':
result=num1*num2;
break;
case '/':
result=(float)num1/(float)num2;
break;
case '%': //mod
result=num1%num2;
break;
default:
printf("Invalid operation.\n");
}
printf("Result: %d %c %d = %.3f\n",num1,opr,num2,result);
return 0;
}


