5-Loops and Program Control in C
C Programming Lessons, Learn C Programming, Introduction to C Language, How to Program with C
In this topic, we will introduce loops in the C programming language. We will see the control of simple programs with the help of these loops.
In programming, loops are used to repeat a specific task (program block) until it is completed.
There are 3 loops used for program control in C.
These are ; for loop, while loop, do-while loop.
Let’s Start with For Loop
The for loop structure easily executes all the details of counter-controlled loops automatically.
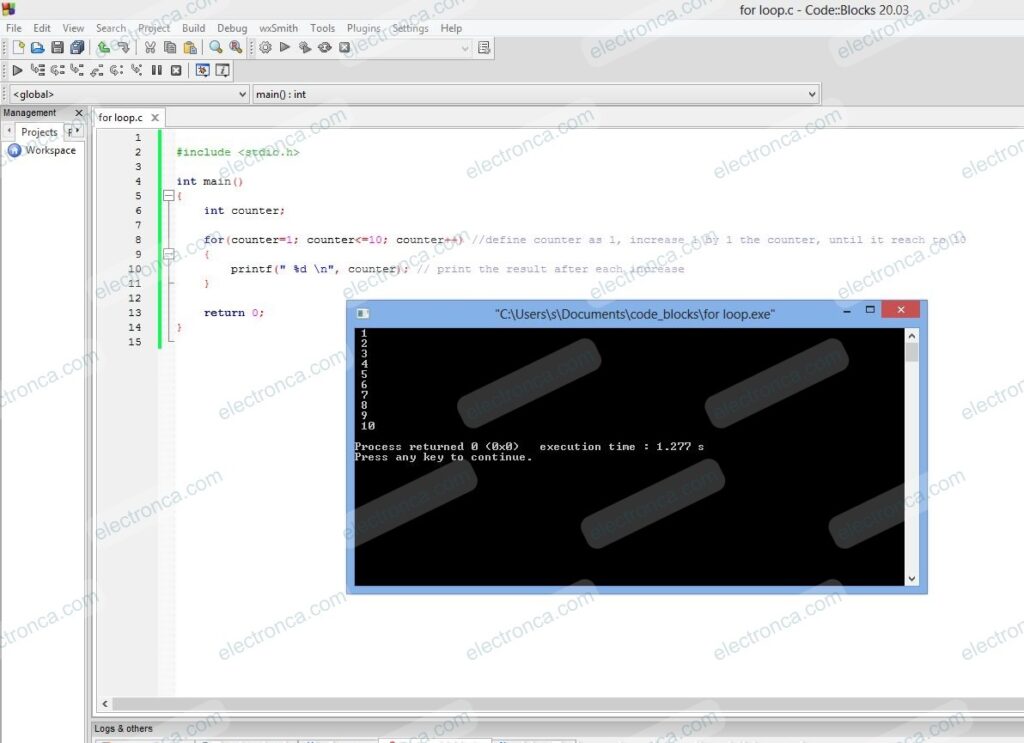
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int counter;
for(counter=1; counter<=10; counter++) //define counter as 1, increase 1 by 1 the counter, until it reach to 10
{
printf(" %d \n", counter); // print the result after each increase
}
return 0;
}
Notes:
1. Let’s assume x=2 , y=10
for(j=x; j<=4*x*y; j+=y/x) is equal to
for(j=2; j<=80; j+=5)
2. increment can be negative (loop variable counts down)
for loop examples
- increase the control variable by 1 from 1 to 100
for(i=0; i <= 100; i++)
- Decrease by 1 from 100 to 1
for(i=100; i <= 1; i- -)
- Increase by 7 from 7 to 77
for(i=7; i <= 77; i +=7)
- Decrease 2 by 2 from 20
for(i=20; i <= 2; i-=2)
- 2,5,8,11,14,17,20
for(i=2; i <= 20; i+=3)
While Loop
As long as the condition is true in the while loop, the same block of code will remain in the loop continuously.
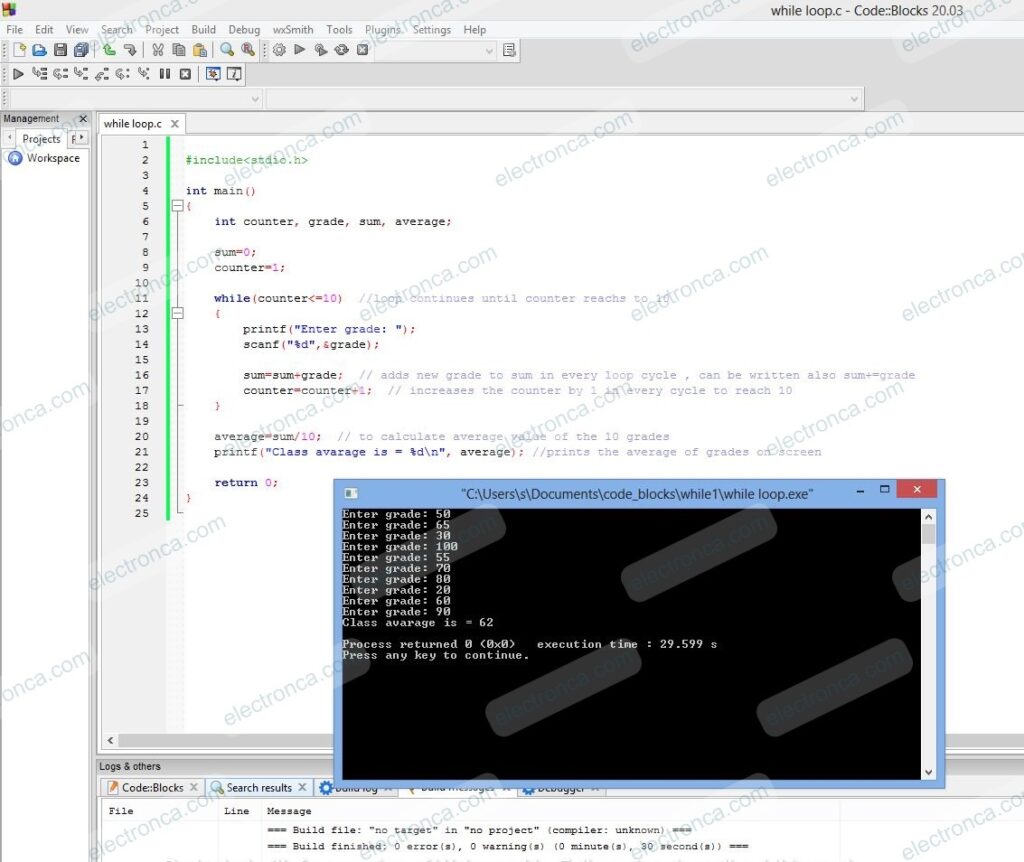
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int counter, grade, sum, average;
sum=0;
counter=1;
while(counter<=10) //loop continues until counter reachs to 10
{
printf("Enter grade: ");
scanf("%d",&grade);
sum=sum+grade; // adds new grade to sum in every loop cycle , can be written also sum+=grade
counter=counter+1; // increases the counter by 1 in every cycle to reach 10
}
average=sum/10; // to calculate average value of the 10 grades
printf("Class avarage is = %d\n", average); //prints the average of grades on screen
return 0;
}
Increment Decrement Operators
(++) single increment, (–) single decrement
pre-increment ++a increments a by 1, and use the new value of a in the statement that a is in
post-increment a++ Use the value of a in the statement that a is in, and then increment a by 1
do-while Loop
In the while structure, the loop continuation condition was tested before the body of the loop.
In the do-while structure, the loop continuation condition is checked after the body of the loop is executed.
When the do-while structure ends, the program continues from the statement after the while statement.
Although curly braces are not needed in do-while, they are used to avoid confusion with while structures.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int counter=1;
do{
printf("%d\n", counter);
}while(++counter <= 10);
return 0;
}
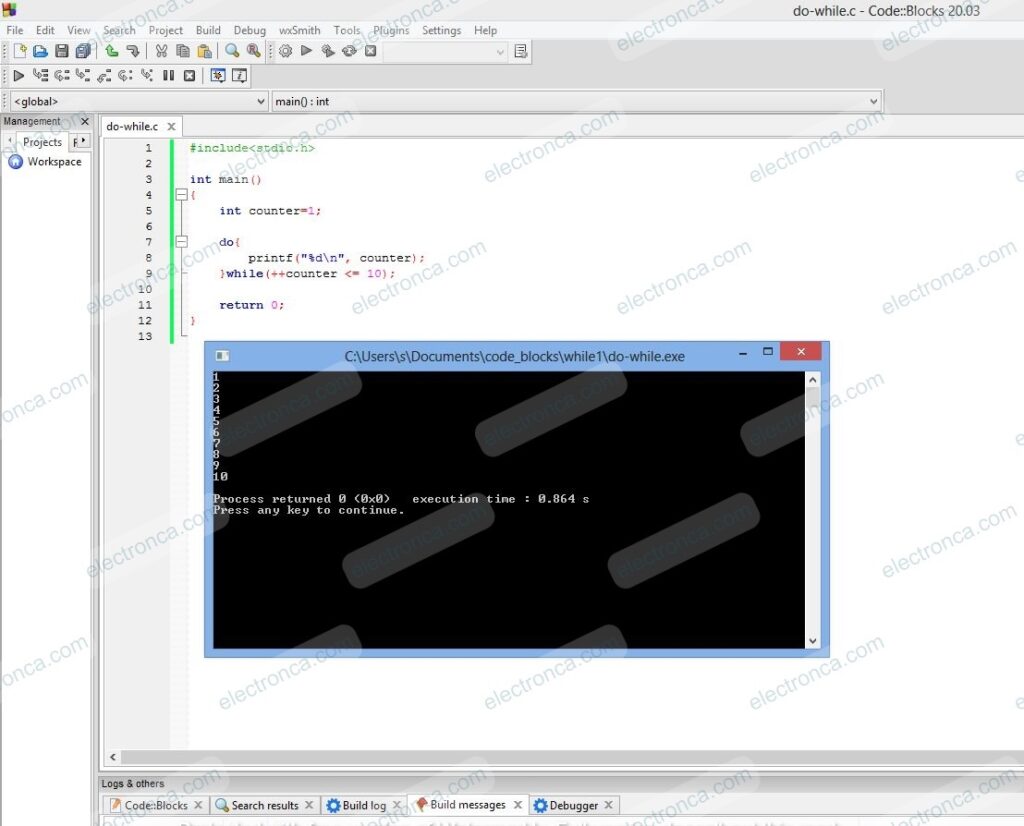
if we set “counter” variable to 10 , program will execute only once and print 10 on screen

Break and Continue Statements
The break statement ends the loop immediately when it is encountered.
The continue statement skips the current iteration of the loop and continues with the next iteration.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x;
for(x=1; x<=10; x++) //loop is set to count until 10
{
if(x==5)
break; //loop counts until it equals to 5 then stop executing
printf("%d\n", x);
}
return 0;
}

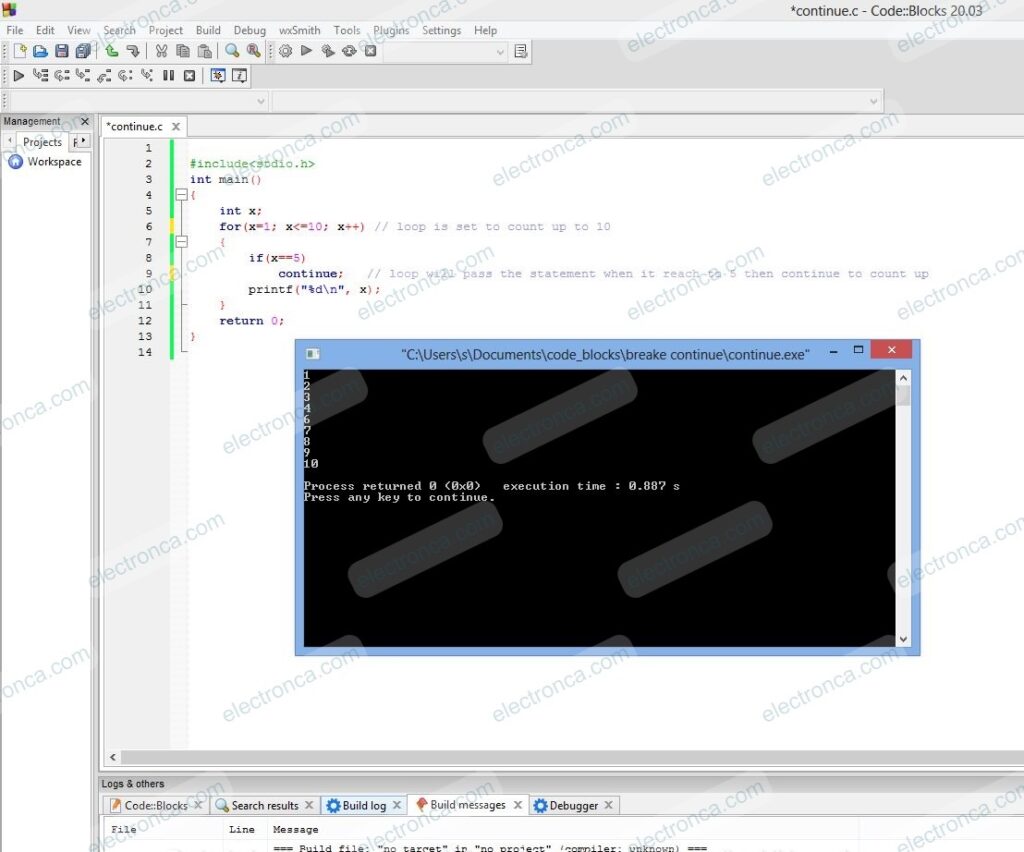
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x;
for(x=1; x<=10; x++) // loop is set to count up to 10
{
if(x==5)
continue; // loop will pass the statement when it reach to 5 then continue to count up
printf("%d\n", x);
}
return 0;
}
In the next lesson, we will make plenty of examples about loops and examine the switch-case structure that we talked about in the previous lesson.

